How CRM Assists in Predictive Analytics
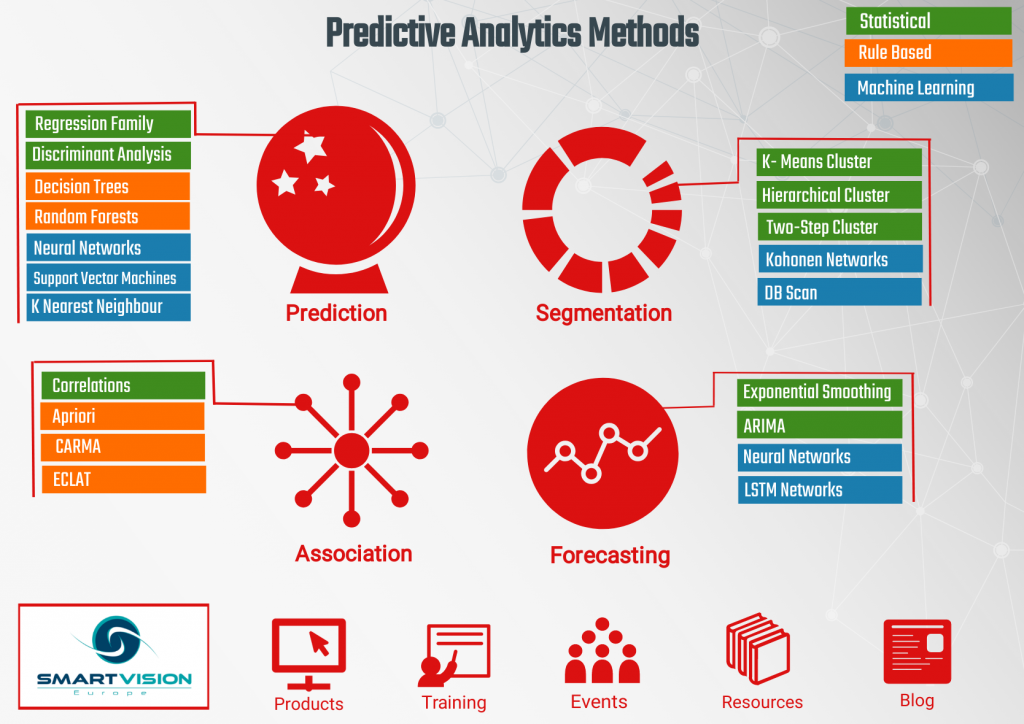
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems have become an integral part of business operations, helping companies manage their interactions with current and potential customers. However, CRM goes beyond just managing customer data; it also plays a crucial role in predictive analytics. By analyzing customer information and behavior patterns, CRM systems can provide valuable insights that help businesses make informed decisions and improve their overall performance.
In this blog article, we will explore how CRM assists in predictive analytics and how businesses can leverage this powerful combination to gain a competitive edge. We will delve into the various ways CRM systems contribute to predictive analytics, including data collection and analysis, customer segmentation, predictive modeling, churn analysis, lead scoring and qualification, sales forecasting, customer lifetime value analysis, personalized marketing campaigns, risk assessment and fraud detection, and continuous improvement and optimization. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how CRM and predictive analytics work hand in hand to drive business success.
Data Collection and Integration
One of the fundamental roles of CRM in predictive analytics is data collection and integration. CRM systems gather valuable customer data from various touchpoints, such as website visits, social media interactions, and email communications. This data is then integrated into a centralized database, providing businesses with a comprehensive view of their customers' activities and preferences.
With CRM, businesses can collect both structured and unstructured data. Structured data includes information such as customer demographics, purchase history, and transaction details. Unstructured data, on the other hand, refers to data from customer interactions, such as customer service calls, emails, and social media posts. By integrating both types of data, CRM systems provide a holistic view of customer behavior and enable businesses to uncover hidden patterns and correlations.
Benefits of Data Collection and Integration
By effectively collecting and integrating customer data through CRM systems, businesses can benefit in several ways:
1. Enhanced Customer Understanding: Data collection and integration allow businesses to gain a deep understanding of their customers' preferences, needs, and behaviors. By analyzing this data, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and correlations that help them better serve their customers.
2. Improved Personalization: With a comprehensive view of customer data, businesses can personalize their interactions and offerings. By understanding individual customer preferences, businesses can tailor marketing messages, recommend relevant products or services, and provide personalized customer service.
3. Better Decision-Making: Data-driven decision-making is crucial for business success. By collecting and integrating customer data, CRM systems provide businesses with valuable insights that inform strategic decisions. This data can help businesses identify market opportunities, optimize marketing campaigns, and allocate resources effectively.
4. Streamlined Operations: By centralizing customer data, CRM systems streamline business operations. With all customer information in one place, businesses can access and analyze data more efficiently, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
Overall, data collection and integration through CRM systems provide businesses with a solid foundation for predictive analytics. The more comprehensive and accurate the data, the more reliable the predictive analytics models and insights.
Customer Segmentation
CRM systems enable businesses to segment their customer base effectively. By categorizing customers into different groups based on demographics, behaviors, or purchase history, businesses can target their marketing efforts more efficiently. This segmentation data can be used in predictive analytics to identify patterns and trends within each customer segment, allowing businesses to personalize their marketing messages and offerings.
Customer segmentation is a powerful tool for businesses as it allows them to understand their customers on a more granular level. By identifying different customer segments, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies and offerings to meet the specific needs and preferences of each segment.
Types of Customer Segmentation
There are various ways businesses can segment their customers using CRM systems:
1. Demographic Segmentation: This segmentation method involves categorizing customers based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, and location. Demographic segmentation helps businesses target their marketing efforts to specific groups that are more likely to be interested in their products or services.
2. Behavioral Segmentation: Behavioral segmentation categorizes customers based on their actions, behaviors, and interactions with the business. This can include purchase history, website visits, engagement on social media, and response to marketing campaigns. By understanding customer behaviors, businesses can personalize their marketing messages and offerings to drive engagement and conversions.
3. Psychographic Segmentation: Psychographic segmentation focuses on customers' attitudes, values, interests, and lifestyles. By understanding customers' motivations and preferences, businesses can create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific psychographic segments.
4. Purchase History Segmentation: This segmentation method categorizes customers based on their past purchase behavior. By analyzing purchase history, businesses can identify high-value customers, frequent buyers, or customers who have not made a purchase in a while. This information helps businesses tailor marketing efforts to re-engage inactive customers or provide special offers to loyal customers.
5. RFM Segmentation: RFM stands for Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value. This segmentation method ranks customers based on these three factors to identify high-value customers who are likely to make repeat purchases. By understanding customer RFM scores, businesses can target their marketing efforts to maximize customer lifetime value and loyalty.
Benefits of Customer Segmentation
Implementing customer segmentation through CRM systems offers several benefits to businesses:
1. More Effective Marketing: By segmenting customers, businesses can create targeted marketing campaigns that are more likely to resonate with specific customer groups. This leads to higher engagement, conversion rates, and return on investment for marketing efforts.
2. Personalized Customer Experiences: Customer segmentation allows businesses to deliver personalized experiences to each customer segment. By tailoring offerings, recommendations, and interactions based on customer preferences, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Improved Product Development: Customer segmentation provides insights into customer preferences and needs, which can inform product development and innovation. By understanding different customer segments, businesses can create products or features that cater to specific customer groups, increasing the chances of success in the market.
4. Enhanced Customer Retention: By segmenting customers, businesses can identify at-risk customers who may be more likely to churn. This allows businesses to implement targeted retention strategies, such as personalized offers or proactive customer service, to reduce churn rates and improve customer retention.
Overall, customer segmentation through CRM systems enables businesses to understand their customers better and tailor their marketing efforts to specific segments. This leads to more effective marketing campaigns, improved customer experiences, and increased customer loyalty.
Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling is a key aspect of predictive analytics, and CRM systems play a crucial role in this process. By leveraging historical customer data, CRM systems can create predictive models that forecast future customer behavior and outcomes. These models help businesses identify potential opportunities, anticipate customer needs, and make data-driven decisions.
Predictive modeling involves using statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and make predictions about future events or behaviors. CRM systems provide the necessary historical customer data for predictive modeling, including past purchases, website interactions, customer service interactions, and more.
Steps in Predictive Modeling
The process of predictive modeling through CRM systems typically involves the following steps:
1. Data Preparation: The first step in predictive modeling is data preparation. This involves cleaning and organizing the historical customer data collected through CRM systems to ensure accuracy and consistency. Data preparation may also involve transforming the data into a format suitable for analysis.
2. Variable Selection: Variable selection is the process of identifying the most relevant variables or features that will be used in the predictive model. CRM systems provide a wide range of customer data, and selecting the right variables is crucial for accurate predictions. This step may involve statistical analysis or machine learning techniques to determine the most influential variables.
3. Model Development: Once the variables are selected, the next step is to develop the predictive model. This step involves applying statistical algorithms or machine learning techniques to the historical customer data to create a model that can predict future outcomes or behaviors. The choice of modeling technique depends on the specific business problem and the nature of the data.
4. Model Evaluation: After developing the predictive model, it is essential to evaluate its performance. This involves testing the model on new data or using cross-validation techniques to assess its accuracy, precision, recall, and other evaluation metrics. Model evaluation helps businesses determine the reliability and effectiveness of the predictive model.
5. Model Deployment and Monitoring: Once the predictive model is deemed satisfactory, it is deployed for use in business operations. CRM systems can integrate the predictive model into their functionalities, allowing businesses to make real-time predictions and recommendations based on customer data. It is crucial to monitor the model'sperformance over time and update it as necessary to ensure its accuracy and relevance.
Benefits of Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling through CRM systems offers several benefits to businesses:
1. Improved Decision-Making: By leveraging predictive models, businesses can make data-driven decisions with a higher level of confidence. Predictive modeling provides insights into future customer behaviors, allowing businesses to allocate resources effectively, identify growth opportunities, and mitigate risks.
2. Anticipating Customer Needs: Predictive models help businesses anticipate customer needs and preferences. By understanding customer behavior patterns, businesses can proactively offer personalized recommendations, promotions, or support, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Targeted Marketing Campaigns: Predictive modeling enables businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer segments. By identifying which customers are more likely to respond positively to certain marketing messages or offers, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts and improve conversion rates.
4. Risk Mitigation: Predictive models can help businesses identify potential risks or issues before they occur. By analyzing customer data, businesses can detect patterns that may indicate fraudulent activities, identify at-risk customers who are likely to churn, or predict potential market fluctuations. This allows businesses to take proactive measures to mitigate risks and protect their interests.
5. Enhanced Customer Experience: Predictive modeling allows businesses to deliver personalized and tailored experiences to their customers. By utilizing customer data, businesses can anticipate customer needs, provide relevant recommendations, and resolve issues in a timely manner, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Overall, predictive modeling through CRM systems empowers businesses to make informed decisions, anticipate customer needs, and optimize their operations. By leveraging historical customer data, businesses can gain a competitive edge by predicting customer behavior and staying ahead of market trends.
Churn Analysis
Churn analysis is the process of identifying customers who are likely to stop using a company's products or services. CRM systems track customer interactions and behaviors, allowing businesses to identify warning signs of potential churn. By analyzing the data collected through CRM, businesses can implement proactive strategies to retain at-risk customers and reduce churn rates.
Churn analysis is essential for businesses as customer retention is often more cost-effective than acquiring new customers. By identifying customers who are at risk of churning, businesses can take targeted actions to address their concerns, improve their experience, and increase the likelihood of retaining them as loyal customers.
Identifying Churn Indicators
CRM systems provide businesses with valuable data to identify churn indicators. These indicators can vary depending on the industry and the specific business, but some common churn indicators include:
1. Decreased Engagement: A decline in customer engagement with a company's products or services can be a sign of potential churn. This can include reduced website visits, decreased usage of a software application, or a decline in interactions with customer support.
2. Complaints or Negative Feedback: Customers who express dissatisfaction or provide negative feedback may be at a higher risk of churning. CRM systems can capture customer complaints or feedback from various channels, such as email, phone calls, or social media, allowing businesses to address their concerns promptly.
3. Inactivity: Customers who have not interacted with a company for a prolonged period may be at risk of churning. CRM systems can track customer activity and identify customers who have not made purchases, logged into their accounts, or engaged with the company in any way.
4. Competitor Interactions: Customers who show signs of engaging with competitors or researching alternative options may be considering switching providers. CRM systems can provide insights into customer interactions with competitors, such as website visits or social media engagements, allowing businesses to take proactive measures to retain these customers.
Churn Prevention Strategies
Once at-risk customers have been identified through churn analysis, businesses can implement various strategies to prevent churn:
1. Personalized Outreach: CRM systems enable businesses to reach out to at-risk customers with personalized messages or offers. By understanding the specific concerns or issues that may be leading to churn, businesses can provide tailored solutions or incentives to encourage customers to stay.
2. Proactive Customer Support: Identifying at-risk customers allows businesses to provide proactive customer support. CRM systems can trigger alerts or notifications when a customer exhibits signs of dissatisfaction or decreased engagement, enabling businesses to reach out and address their concerns promptly.
3. Loyalty Programs: Implementing loyalty programs can incentivize at-risk customers to stay. CRM systems can help businesses identify customers who may benefit from loyalty programs and track their participation and engagement with the program.
4. Customer Feedback: CRM systems can facilitate the collection of customer feedback, allowing businesses to understand the underlying reasons for potential churn. By actively seeking customer feedback, businesses can identify areas for improvement and implement changes to address customer concerns.
Churn analysis through CRM systems helps businesses proactively identify and address customer churn. By implementing targeted strategies to retain at-risk customers, businesses can improve customer loyalty, reduce customer acquisition costs, and ultimately increase their bottom line.
Lead Scoring and Qualification
CRM systems aid in lead scoring and qualification, which helps businesses prioritize their sales efforts. By analyzing customer data, CRM systems assign scores to leads based on their likelihood of converting into customers. This scoring process enables sales teams to focus their time and resources on high-value leads, increasing their chances of closing deals and generating revenue.
Lead scoring and qualification through CRM systems involve evaluating various factors to determine the quality and potential value of a lead. These factors can include demographic information, engagement levels, purchase history, or any other relevant data collected through CRM systems.
The Lead Scoring Process
The lead scoring process typically involves the following steps:
1. Define Lead Scoring Criteria: The first step is to define the criteria that will be used to score leads. This can include factors such as company size, industry, job title, engagement levels, or any other relevant information. CRM systems allow businesses to set up automated rules or algorithms to assign scores based on these criteria.
2. Assign Scores: Once the lead scoring criteria are defined, CRM systems assign scores to each lead based on the identified factors. The scoring can be done on a numerical scale or using other methods such as letter grades or categories.
3. Prioritize Leads: After assigning scores, CRM systems prioritize leads based on their scores. High-scoring leads are considered more likely to convert and are given higher priority for sales outreach and follow-up.
4. Nurture Low-Scoring Leads: Leads with lower scores are not discarded but are instead placed in lead nurturing campaigns. CRM systems can automate personalized marketing campaigns or follow-up sequences to nurture these leads and move them closer to conversion.
Benefits of Lead Scoring and Qualification
The use of lead scoring and qualification through CRM systems offers several benefits to businesses:
1. Efficient Sales Efforts: Lead scoring allows sales teams to focus their efforts on leads with the highest potential, increasing efficiency and productivity. By prioritizing high-scoring leads, sales teams can allocate their time and resources more effectively, resulting in higher conversion rates and revenue generation.
2. Improved Lead Conversion: By targeting high-quality leads, businesses increase their chances of converting leads into customers. Lead scoring helps identify leads that are more likely to be interested in the company's products or services, enabling sales teams to tailor their sales pitches and communication to meet the specific needs of each lead.
3. Personalized Marketing: Lead scoring provides insights into the interests and preferences of leads, allowing businesses to personalize their marketing messages and offerings. CRM systems enable businesses to segment leads based on their scores and create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with each lead segment.
4. Better Sales and Marketing Alignment: Lead scoring facilitates better alignment between sales and marketing teams. By using CRM systems, sales teams can provide feedback on lead quality and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, allowing marketing teams to optimize their strategies and improve lead generation efforts.
Lead scoring and qualification through CRM systems help businesses optimize their sales efforts by prioritizing high-value leads and tailoring marketing messages. By focusing on leads with the highest potential, businesses can improve conversion rates, generate more revenue, and enhance the overall efficiency of their sales processes.
Sales Forecasting
CRM systems provide valuable insights for sales forecasting, empowering businesses to make accurate predictions about future sales performance. By analyzing historical sales data, CRM systems can identify trends, seasonality, and other factors that impact sales. This information allows businesses to develop realistic sales targets, allocate resources effectively, and make informed decisions to drive revenue growth.
Sales forecasting is a critical aspect of businessstrategy as it helps businesses plan and make informed decisions. By leveraging CRM systems for sales forecasting, businesses can gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and other factors that influence sales performance.
The Sales Forecasting Process
The sales forecasting process typically involves the following steps:
1. Data Collection and Analysis: CRM systems provide businesses with a wealth of historical sales data, including revenue, quantity, and other relevant metrics. This data is collected and analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and seasonality in sales performance.
2. Historical Sales Analysis: By analyzing historical sales data, CRM systems can provide insights into past sales performance, identifying factors that influenced success or failure. This analysis helps businesses understand the impact of marketing campaigns, pricing strategies, seasonality, or external factors on sales.
3. Market Analysis: CRM systems can integrate external data sources, such as market research reports or industry trends, to provide a broader perspective on the market. By analyzing market conditions and customer behaviors, businesses can make more accurate sales forecasts and adjust their strategies accordingly.
4. Forecasting Methodology: CRM systems enable businesses to apply various forecasting methodologies, such as time series analysis, regression analysis, or predictive modeling, to predict future sales. The choice of methodology depends on the nature of the business, available data, and the level of accuracy required.
5. Setting Sales Targets: Based on the sales forecast, businesses can set realistic sales targets for specific time periods. CRM systems allow businesses to track progress towards these targets and make adjustments as necessary.
Benefits of Sales Forecasting
The use of CRM systems for sales forecasting offers several benefits to businesses:
1. Informed Decision-Making: Sales forecasting provides businesses with insights into future sales performance, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, inventory management, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns.
2. Resource Allocation: By accurately forecasting sales, businesses can allocate resources, such as inventory, staff, or marketing budgets, more effectively. This optimization leads to cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
3. Budgeting and Financial Planning: Sales forecasting helps businesses develop realistic budgets and financial plans. By understanding future revenue projections, businesses can plan their expenses, investments, and growth strategies accordingly.
4. Sales Team Performance: Sales forecasting enables businesses to evaluate and incentivize sales team performance. By setting achievable sales targets based on forecasts, businesses can motivate and reward sales teams for meeting or exceeding expectations.
5. Market Opportunity Identification: Sales forecasting helps businesses identify emerging market opportunities or potential gaps in their product or service offerings. By analyzing sales trends and market conditions, businesses can make strategic decisions to capitalize on new opportunities.
Overall, sales forecasting through CRM systems empowers businesses to plan, make informed decisions, and optimize their sales strategies. By leveraging historical data and market insights, businesses can set realistic sales targets, allocate resources effectively, and drive revenue growth.
Customer Lifetime Value Analysis
CRM systems assist in analyzing customer lifetime value (CLV), which is a crucial metric for businesses. By analyzing customer data and purchase history, CRM systems can calculate the potential revenue each customer is likely to generate over their lifetime. This information helps businesses segment customers based on their value and allocate resources accordingly, focusing on high-value customers to maximize profitability.
Customer lifetime value is a measure of the total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with a business. By understanding the CLV of individual customers, businesses can make informed decisions regarding acquisition costs, retention strategies, and customer relationship management.
Calculating Customer Lifetime Value
The calculation of customer lifetime value typically involves the following steps:
1. Data Collection: CRM systems collect and store customer data, including purchase history, frequency of purchases, average order value, and customer retention information. This data is used as the basis for calculating CLV.
2. Segmentation: CRM systems enable businesses to segment customers based on various factors, such as purchase frequency, order value, or engagement levels. This segmentation helps identify high-value customers who are likely to contribute significantly to CLV.
3. Calculation: CLV can be calculated using different methodologies, such as the historical method or the predictive method. The historical method calculates CLV based on past customer behavior and purchase history, while the predictive method uses statistical models or machine learning algorithms to forecast future customer behavior.
4. Analysis and Insights: Once CLV is calculated, CRM systems provide businesses with insights into customer segments and their contribution to overall revenue. This analysis helps businesses make decisions regarding resource allocation, retention strategies, and customer acquisition efforts.
Benefits of Customer Lifetime Value Analysis
Customer lifetime value analysis through CRM systems offers several benefits to businesses:
1. Resource Allocation: By understanding the value of individual customers, businesses can allocate resources more effectively. High-value customers can receive personalized attention and tailored offerings, while low-value customers can be targeted with cost-effective retention strategies or marketing campaigns.
2. Customer Retention: Customer lifetime value analysis helps businesses identify at-risk customers with a high CLV. By implementing targeted retention strategies, such as loyalty programs, personalized offers, or proactive customer service, businesses can increase customer retention rates and maximize their CLV.
3. Customer Acquisition Strategies: By analyzing CLV, businesses can make more informed decisions regarding customer acquisition costs and strategies. Businesses can focus their acquisition efforts on customer segments with higher CLV potential, optimizing their marketing budgets and increasing return on investment.
4. Pricing and Discount Strategies: CLV analysis enables businesses to develop pricing and discount strategies that align with customer value. High-value customers may be willing to pay premium prices, while lower-value customers may respond better to discounts or promotions.
5. Customer Segmentation and Personalization: Customer lifetime value analysis helps businesses segment customers based on their value and preferences. By understanding the value of individual customers, businesses can tailor their marketing messages, product recommendations, and customer experiences to maximize customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Customer lifetime value analysis through CRM systems provides businesses with valuable insights into customer value and helps them make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, retention strategies, and customer acquisition efforts. By focusing on high-value customers and maximizing their CLV, businesses can drive profitability and long-term success.
Personalized Marketing Campaigns
CRM systems enable businesses to create personalized marketing campaigns based on customer data and predictive analytics. By understanding customer preferences and behaviors, businesses can tailor their marketing messages, offers, and recommendations to each individual customer. This level of personalization enhances customer engagement, improves conversion rates, and fosters long-term customer loyalty.
Personalized marketing campaigns leverage CRM systems' capabilities to collect and analyze customer data, enabling businesses to deliver targeted and relevant marketing messages. By understanding customer preferences and behaviors, businesses can create highly personalized campaigns that resonate with individual customers.
Steps in Personalized Marketing Campaigns
The process of creating personalized marketing campaigns through CRM systems typically involves the following steps:
1. Customer Data Collection: CRM systems collect and store customer data from various touchpoints, such as website visits, email interactions, social media engagements, and purchase history. This data forms the foundation for personalized marketing campaigns.
2. Customer Segmentation: CRM systems enable businesses to segment their customer base based on various factors, such as demographics, purchase behavior, or engagement levels. Customer segmentation helps businesses understand the different needs and preferences of their customers.
3. Data Analysis and Insights: By analyzing customer data, CRM systems provide businesses with insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and trends. These insights inform the development of personalized marketing campaigns and messages.
4. Campaign Customization: Based on customer insights, businesses can customize marketing campaigns to target specific customer segments. This customization can include personalized email messages, product recommendations, or tailored offers that align with individual customer preferences.
5. Automation and Delivery: CRM systems enable businesses to automate the delivery of personalized marketing campaigns. With automation, businesses can send targeted messages at the right time, ensuring that customers receive relevant offers and recommendations when they are most likely to engage.
Benefits of Personalized Marketing Campaigns
The use of personalized marketing campaigns through CRM systems offers several benefits to businesses:
1. Increased Customer Engagement: Personalized marketing campaigns resonate with customers on a deeper level, increasing their engagement and interest in the business. By delivering relevant and tailored messages, businesses can capture customer attention and encourage interaction.
2. Improved Conversion Rates: Personalized marketing campaigns have higher conversion rates compared to generic, one-size-fits-all marketing messages. By addressing individual customer needs and preferences, businesses can increase the likelihood of customers making a purchaseor taking a desired action, ultimately improving conversion rates and driving revenue.
3. Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalized marketing campaigns show customers that businesses understand their unique needs and preferences. By delivering personalized offers, recommendations, and experiences, businesses can create a positive and memorable customer experience, fostering customer loyalty and advocacy.
4. Increased Customer Lifetime Value: Personalized marketing campaigns help businesses strengthen customer relationships and increase customer lifetime value. By delivering personalized offers and recommendations, businesses can encourage repeat purchases, cross-selling, and upselling, maximizing the revenue potential of each customer.
5. Efficient Resource Allocation: Personalized marketing campaigns allow businesses to allocate their marketing resources more effectively. By targeting specific customer segments with personalized messages, businesses can optimize their marketing budgets and achieve a higher return on investment.
Overall, personalized marketing campaigns through CRM systems enable businesses to deliver targeted and relevant messages to individual customers. By leveraging customer data and insights, businesses can enhance customer engagement, improve conversion rates, and foster long-term customer loyalty.
Risk Assessment and Fraud Detection
CRM systems contribute to risk assessment and fraud detection by analyzing customer data for suspicious activities or patterns. By monitoring customer behavior and transaction history, CRM systems can identify potential fraudulent activities and mitigate risks. This proactive approach helps businesses protect their assets, maintain customer trust, and minimize financial losses.
Risk assessment and fraud detection are critical components of business operations, particularly in industries where fraudulent activities can have significant financial or reputational consequences. CRM systems provide businesses with the tools and capabilities to identify and address potential risks and fraud proactively.
Identifying Risk and Fraud Indicators
CRM systems can help businesses identify risk and fraud indicators by analyzing customer data and transaction history. Some common risk and fraud indicators include:
1. Unusual Account Activity: CRM systems can detect unusual account activity, such as a sudden increase in purchase volume, multiple transactions within a short period, or transactions that deviate from a customer's typical behavior. These activities may indicate potential fraudulent activities or account compromise.
2. Inconsistent Information: CRM systems can flag inconsistencies or discrepancies in customer information, such as mismatched addresses, contact details, or payment information. These inconsistencies may indicate attempts to defraud the business or engage in illicit activities.
3. Anomalous Behavior: CRM systems can identify anomalous customer behavior, such as frequent changes in account details, multiple failed login attempts, or unusual IP addresses associated with account access. These behaviors may indicate unauthorized access or fraudulent activities.
4. Unusual Transaction Patterns: CRM systems can detect unusual transaction patterns, such as large or frequent purchases made outside a customer's normal behavior, transactions involving high-risk countries or regions, or transactions that trigger predefined risk thresholds. These patterns may indicate potential fraudulent activities or money laundering.
Risk Mitigation and Fraud Prevention
Once risk and fraud indicators are identified through CRM systems, businesses can implement strategies to mitigate these risks and prevent fraud:
1. Enhanced Security Measures: CRM systems enable businesses to implement robust security measures, such as two-factor authentication, encryption, and secure payment gateways. These measures help protect customer data and minimize the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
2. Real-time Monitoring: CRM systems can provide real-time monitoring of customer activities and transactions. By continuously monitoring customer behavior, businesses can detect and respond to potential risks and fraudulent activities promptly.
3. Fraud Detection Algorithms: CRM systems can leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to detect patterns and anomalies associated with fraud. By analyzing historical data and customer behavior, these algorithms can identify potential fraudulent activities and trigger alerts for further investigation.
4. Fraud Prevention Policies: CRM systems enable businesses to implement fraud prevention policies and procedures. These policies can include transaction verification processes, customer identity verification, or predefined risk thresholds that trigger additional scrutiny for high-risk transactions.
By leveraging CRM systems for risk assessment and fraud detection, businesses can proactively protect their assets, safeguard customer data, and maintain trust and credibility. Through continuous monitoring and the implementation of robust security measures, businesses can minimize financial losses and reputational damage associated with fraud and illicit activities.
Continuous Improvement and Optimization
CRM systems play a vital role in continuous improvement and optimization by providing valuable feedback and insights. By analyzing customer data and predictive analytics, businesses can identify areas for improvement in their sales processes, customer service, and overall operations. This information helps businesses make data-driven decisions to enhance efficiency, customer satisfaction, and business performance.
Continuous improvement and optimization are essential for businesses to stay competitive and meet evolving customer expectations. CRM systems provide businesses with the necessary tools and capabilities to collect and analyze customer data, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to drive operational excellence.
Identifying Improvement Opportunities
CRM systems help businesses identify improvement opportunities by analyzing customer data and performance metrics. Some areas where improvement opportunities may arise include:
1. Sales Processes: CRM systems can analyze sales data to identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the sales process. This analysis may uncover areas where sales cycles can be shortened, conversion rates can be improved, or sales team performance can be optimized.
2. Customer Service: CRM systems provide insights into customer interactions and satisfaction levels. By analyzing customer service data, businesses can identify areas where customer service can be enhanced, response times can be improved, or support processes can be streamlined.
3. Marketing Campaigns: CRM systems enable businesses to analyze the performance of marketing campaigns. By tracking campaign metrics, businesses can identify areas where marketing efforts can be optimized, such as targeting specific customer segments, refining messaging, or adjusting media channels.
4. Product Development: CRM systems provide valuable feedback on customer preferences, needs, and behaviors. By analyzing customer data, businesses can identify areas for product improvement, new features or offerings, or opportunities for innovation.
Implementing Continuous Improvement
Once improvement opportunities are identified through CRM systems, businesses can implement strategies to drive continuous improvement:
1. Data-Driven Decision-Making: CRM systems enable businesses to make data-driven decisions by providing insights based on customer data and predictive analytics. By leveraging this information, businesses can prioritize improvement initiatives and allocate resources effectively.
2. Process Optimization: CRM systems can help businesses streamline processes and workflows. By identifying bottlenecks or inefficiencies, businesses can implement process improvements, automate repetitive tasks, and optimize resource allocation.
3. Training and Development: CRM systems provide insights into sales team performance and customer interactions. By analyzing this data, businesses can identify areas where training and development programs can be implemented to enhance skills, improve customer engagement, and drive sales effectiveness.
4. Customer Feedback and Engagement: CRM systems facilitate the collection of customer feedback and enable businesses to engage customers in meaningful ways. By actively seeking customer input, businesses can uncover areas for improvement, address customer concerns, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Continuous improvement and optimization through CRM systems help businesses stay agile, customer-centric, and competitive. By leveraging customer data and insights, businesses can make informed decisions, streamline processes, and enhance customer experiences, ultimately driving business success and growth.
In conclusion, CRM systems are not just tools for managing customer relationships; they are powerful allies in predictive analytics. By leveraging the vast amount of customer data they collect, CRM systems enable businesses to gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and drive growth. From data collection and integration to personalized marketing campaigns and continuous improvement, CRM systems play a crucial role in enhancing business performance and achieving success in today's competitive landscape.
Post a Comment for "How CRM Assists in Predictive Analytics"